Lung surgery is a medical procedure that involves operating on the lungs to treat various conditions. Here's some information about lung surgery in simple words:
Lung Cancer: Lung surgery is often performed to remove tumors or cancerous growths from the lungs. It helps treat lung cancer and prevent its spread.
Lung Infections: In severe cases of lung infections or abscesses, surgery may be necessary to remove infected lung tissue and improve lung function.
Lung Biopsy:Lung Biopsy: Sometimes, doctors need to examine lung tissue to diagnose certain lung diseases or cancer. Lung surgery can be done to obtain a small tissue sample for testing.
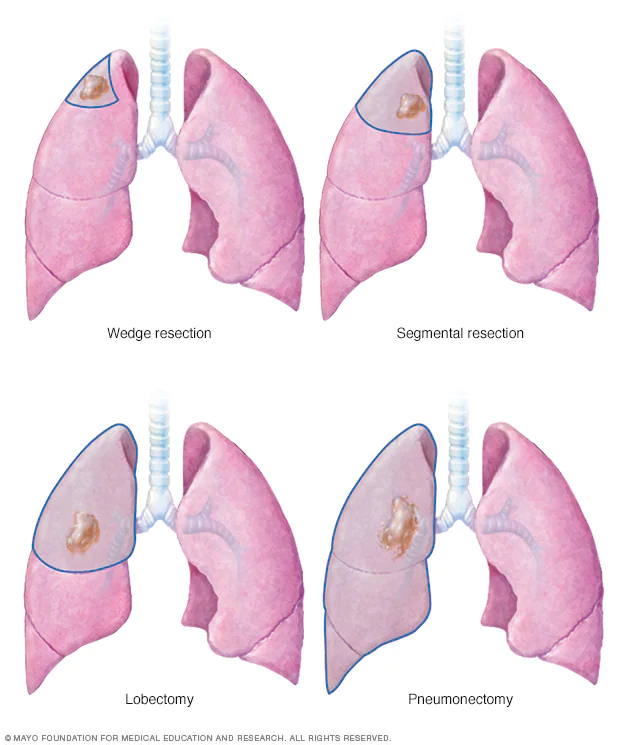
Lobectomy: This involves removing an entire lobe (section) of the lung. It's commonly used for lung cancer treatment.
Wedge Resection: In a wedge resection, a small, wedge-shaped piece of the lung containing the tumor is removed. It's used for small tumors.
Pneumonectomy:A pneumonectomy is the removal of an entire lung. It's usually done in more advanced lung cancer cases.
The recovery time after lung surgery varies depending on the type of surgery and the patient's health. Some patients stay in the hospital for a few days to a week for post-operative care.
As with any surgery, lung surgery carries risks, such as bleeding, infection, complications related to anesthesia, and damage to nearby structures. However, skilled surgeons minimize these risks.
Lung surgery involves procedures performed on the lungs to treat lung cancer, infections, and other lung conditions. The surgery can improve lung function and overall health. If you or someone you know requires lung surgery, it's essential to discuss the options and potential risks with a qualified healthcare professional.